Client Background
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses often face the need to scale their AWS infrastructure due to growth and increased demand for their applications. With a surge in business and a significant influx of requests, it becomes crucial to efficiently manage multiple applications by scaling instances and attaching multiple target groups. This blog post explores into the challenges encountered in such scenarios and provides effective strategies for achieving scalable instances and seamless management of multiple target groups and maintaining the same IP address for the instance.
Challenge
One of the primary challenges involves ensuring that each application operates on a different port and is linked to its corresponding target group. This requirement adds complexity to the scaling process, as scaling the instance necessitates attaching the appropriate target groups to ensure effective traffic distribution among the applications. Additionally, maintaining the same IP address for the instance further adds to the challenges faced.
Solution
we have developed a shell script that automates the process of starting instances and attaching the appropriate target groups and maintaining the same IP address for the instance, saving time and effort. This solution allows us to dynamically scale up instances when high utilization is detected, ensuring optimal performance for our applications.
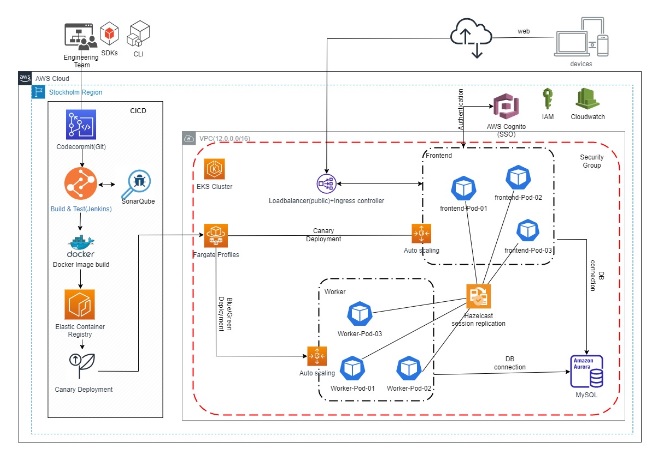
Shell Script Automation: To simplify the scaling/scale-out and target group attachment/deregister process, we have developed a shell script that handles the entire workflow. This script can be executed manually or scheduled or invoke Cloudwatch alarms to run, depending on the anticipated workload changes.
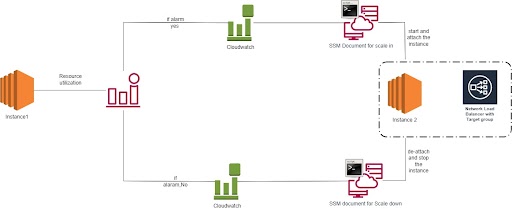
we will demonstrate how to execute a shell script remotely from an EC2 instance using Amazon EventBridge rules and the SSM Run Command document. Instead of utilizing auto scaling, we will start an EC2 instance and register its two target groups with a load balancer when a CloudWatch alarm is triggered due to high CPU utilization exceeding 80%. The following steps outline the configuration and functionality of this solution.
- Configure CloudWatch Alarm: First, we set up a CloudWatch alarm to monitor CPU utilization on the EC2 instance. The alarm threshold is set at 80%, which will trigger an alarm state change when exceeded.
- Set Up EventBridge Rule: Next, we create an EventBridge rule with an event pattern that matches the CloudWatch alarm state change event. This rule specifies that when the alarm state changes, EventBridge should send the event to the specified target, which is an SSM Run Command document.
- Configure SSM Run Command Document: We create an SSM Run Command document that defines the shell script we want to execute remotely on the EC2 instance. This document specifies the commands, parameters, and any required inputs for the script.
- Start EC2 Instance and Attach Target Groups: When the CloudWatch alarm state changes due to CPU utilization exceeding 80%, CloudWatch sends the event to EventBridge. EventBridge then matches the event pattern defined in the rule and forwards the event to the specified target, which is the SSM Run Command document.
- Execution of Shell Script: The SSM Run Command document receives the event and executes the defined shell script remotely on the EC2 instance. The script starts the EC2 instance and registers its two target groups with the load balancer, ensuring that traffic can be properly routed.
- Verification and Optimization: After the shell script is executed, we verify that the EC2 instance has started and the target groups have been successfully registered with the load balancer. We can monitor the CPU utilization and load balancing to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
- Creating IAM role and attach With EC2
- Deploy script for Start/stop the VM and attach the target Group with Load balancerin any ec2 insatance. Then add the ec2 instance in SSM fleet
- Cloudwatch Alarm setup for monitor CPU Utilisation
- Creating own SSM RUN Command Document
- Amazon Eventbridge Rule integration with SSM.
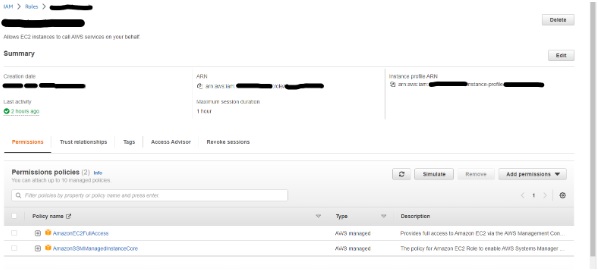
Creating IAM role and attach With EC2
Create IAM Role and add the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore (which is used to SSM agent integration with SSM ) and AmazonEc2FullAccess (Which is used to start the instance and register with Load balancer ) Policy.
Here I took an Ubuntu 20.04.5 OS instance. AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) is preinstalled on some Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) provided by AWS (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/latest/userguide/ami-preinstalled-agent.html). We can verify the ssm agent installed and running status by command “systemctl status snap.amazon-ssm-agent.amazon-ssm-agent.service”.
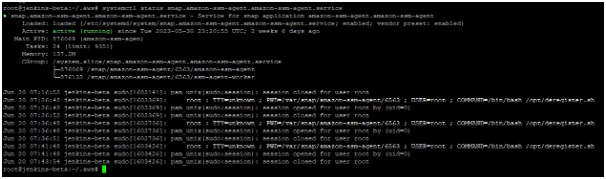
Once we have attached an IAM role with EC2 , then communication will be established with SSM.
Script for Start/stop the VM and attach/de-attch the target Group with Load balancer.
In this script, we utilize one EC2 instance, two target groups for two applications, and one load balancer. The script follows a sequence of steps: it starts the EC2 instance and checks the status of both applications. If both applications return a 200 response, indicating they are running correctly, the script proceeds to register both target groups with the load balancer.
It deregisters the EC2 instance and checks deregistering process of both target groups . If both target groups return an “unused” response, indicating they are deregister correctly, the script proceeds to stop the instance.
Above mention the script download en deploy any one server , the script will invoke and trigger via SSM
Cloudwatch Alarm setup for monitor CPU Utilisation
We have configured a CloudWatch alarm for CPU Utilization greater than 80% for at least 1 data point within a 5-minute interval.
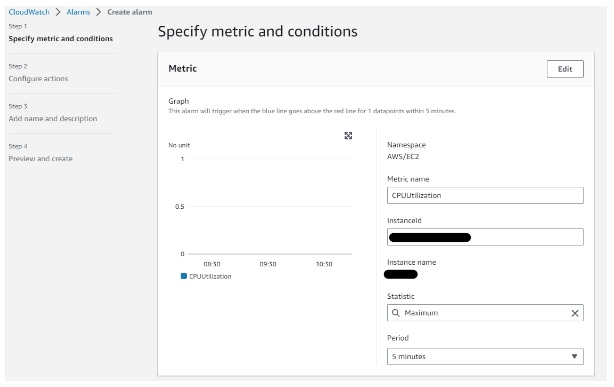
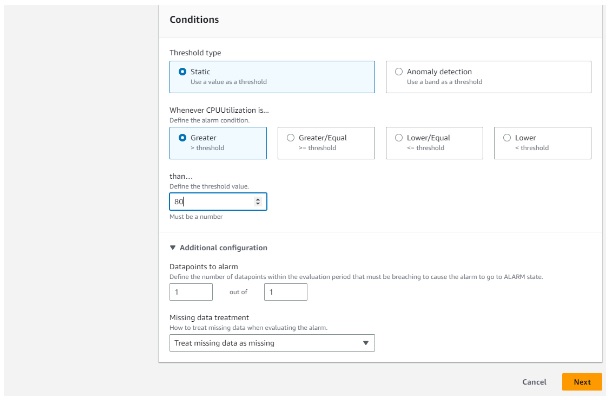
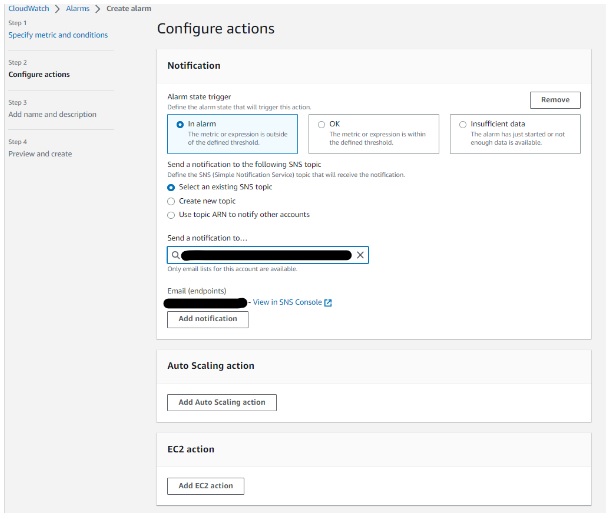
Then provide the alarm name, review and create an alarm.
Creating own SSM RUN Command Document
AS we need to run shell scripts in Ec2. We need to create our own document.
Open System manager console and Navigate to shared Resources, Documents, Owned by me and then click create document -> Command and session
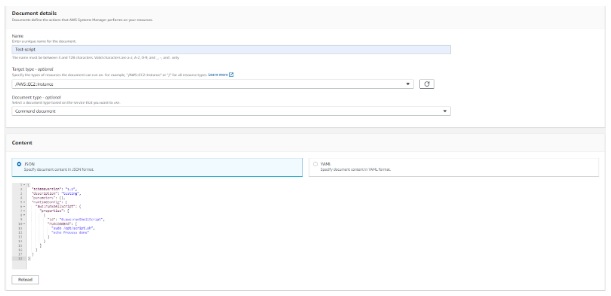
We can use the below json file to create a document and modify the run command as per need.
{
"schemaVersion": "1.2",
"description": "testing",
"parameters": {},
"runtimeConfig": {
"aws:runShellScript": {
"properties": [
{
"id": "0.aws:runShellScript",
"runCommand": [
"Sudo /opt/start_instance_attach_targetgroup.sh",
"echo Process restarted "
]
}
]
}
}
}
Amazon Eventbridge Rule integration with SSM
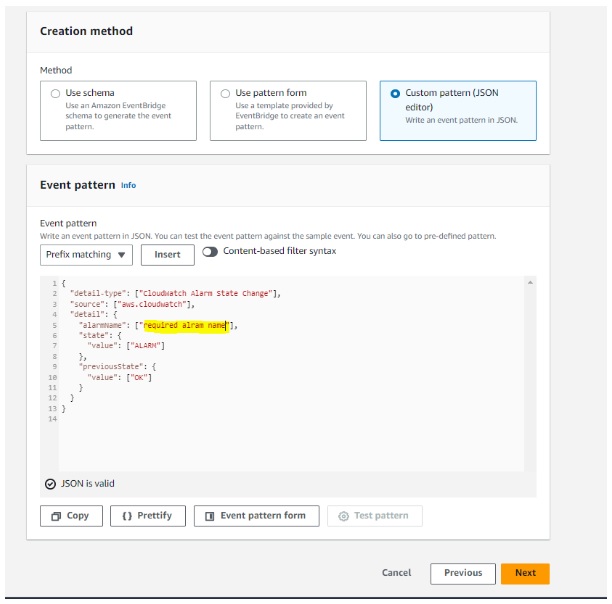
We can use the below json file for the event pattern, which will help us to get cloudwatch alarm events. Modify Alarm name.
{
"detail-type": ["CloudWatch Alarm State Change"],
"source": ["aws.cloudwatch"],
"detail": {
"alarmName": ["required alarm name"],
"state": {
"value": ["ALARM"]
},
"previousState": {
"value": ["OK"]
}
}
}
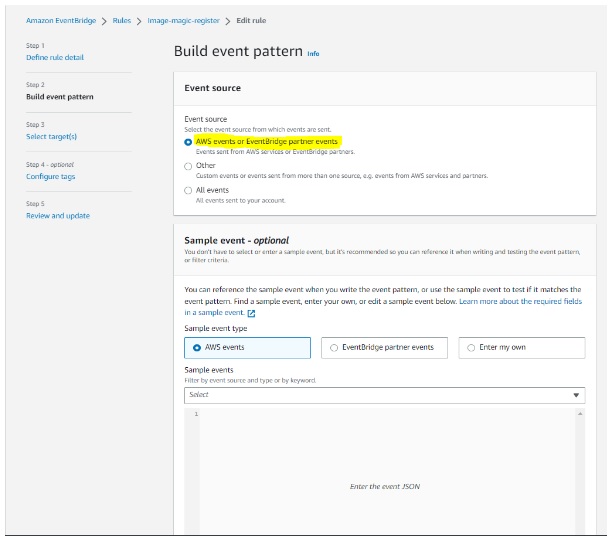
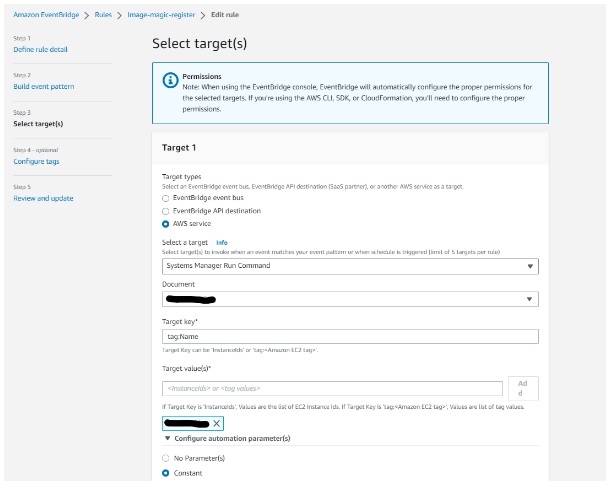
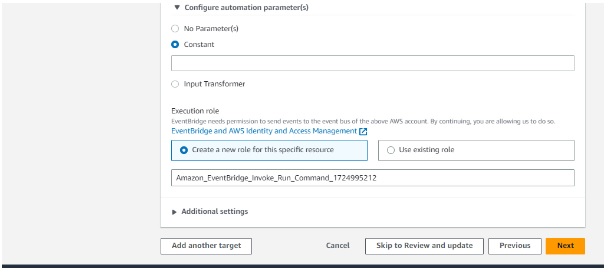
Then Review and create a new rule.
Similarly, if the resource utilization returns to normal, the script can initiate the deregistration process. It will revoke the instance from the target groups and subsequently stop the instance.
Conclusion
Scaling/scale down instances and attaching multiple target groups in AWS is essential for accommodating business growth and efficiently managing multiple applications. Implementing these strategies will enable organizations to meet the increasing demands of their applications and provide a seamless user experience, If you have any trouble in implementing this please contact us on info@idevopz.com
